Introduction to the Kamchatka Peninsula Earthquake Events
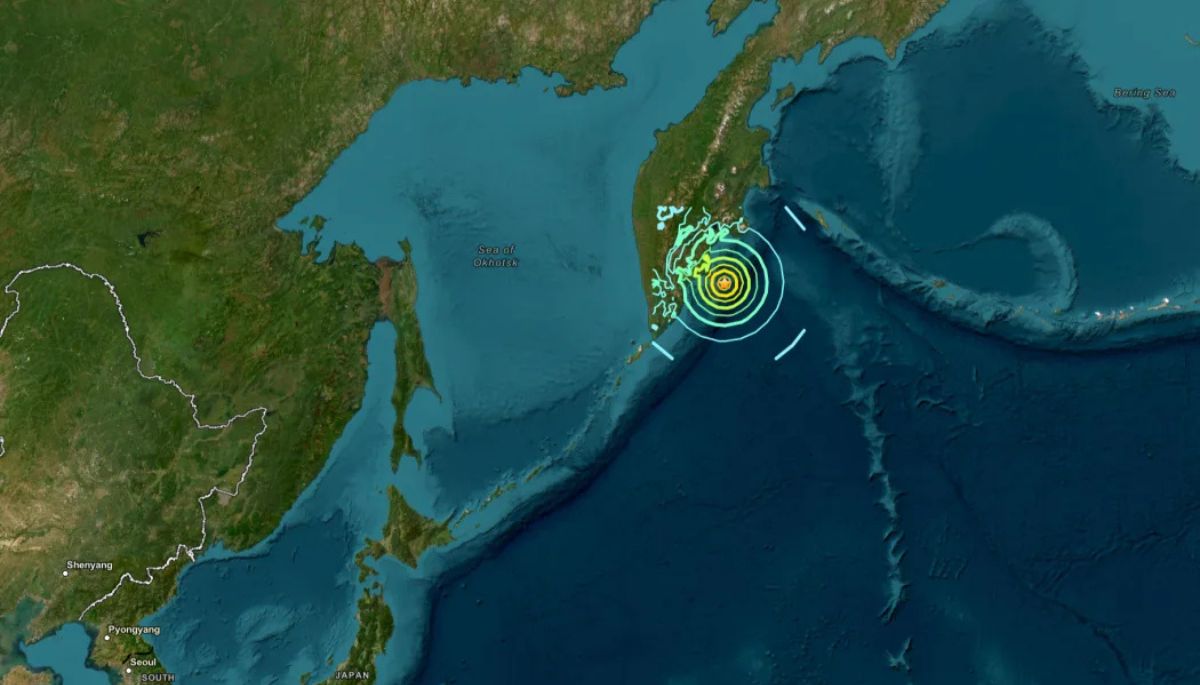
On Sunday, July 20, 2025, the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia’s Far East was rocked by a series of powerful earthquakes, with the strongest reaching a magnitude of 7.4. These seismic events, centered approximately 144 kilometers east of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, a city with a population of around 180,000, triggered immediate concern about potential tsunami waves along Russia’s Pacific coast. The Pacific Tsunami Warning Center (PTWC) initially issued a warning for significant tsunami activity but later downgraded it, forecasting waves of up to one meter.
This Kamchatka Peninsula earthquake and tsunami warning event has drawn global attention due to the region’s history of seismic activity and its potential for widespread impact. In this article, we’ll explore the details of these earthquakes, their implications, and what residents and authorities are doing to stay prepared.
Understanding the Kamchatka Peninsula Earthquakes
The Kamchatka Peninsula, located along the Pacific Ring of Fire, is no stranger to seismic activity. This region is home to numerous active volcanoes and experiences frequent earthquakes due to its position at the convergence of tectonic plates. On July 20, 2025, five powerful earthquakes struck offshore, with the most significant registering a magnitude of 7.4. According to the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), this quake occurred at a depth of 20 kilometers, approximately 144 kilometers east of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. Just minutes earlier, a 6.7-magnitude quake was recorded in the same area, adding to the intensity of the event.
The sequence of quakes began with the 6.7-magnitude tremor, followed shortly by the more powerful 7.4-magnitude event. The USGS reported that the epicenter of the larger quake was situated in the Pacific Ocean, at a relatively shallow depth of 20 kilometers. Shallow earthquakes, like this one, often pose a greater risk of generating tsunamis because they can displace large volumes of seawater. The proximity of these quakes to Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, a major population center, heightened concerns about potential damage and the need for swift action.
Tsunami Warning and Response
Following the earthquakes, the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center issued an immediate threat forecast for the Kamchatka Peninsula, warning of the possibility of major tsunami waves. The initial alert caused alarm among residents and authorities, given the region’s history of destructive tsunamis. However, after further analysis, the PTWC downgraded the warning, stating that waves of up to one meter (approximately 3.3 feet) could occur along the coast. While this was a significant relief, the potential for even small tsunami waves prompted Russia’s Emergencies Ministry to issue its own tsunami warning, urging residents of coastal settlements to stay away from the shoreline.
The swift response from both the PTWC and Russia’s Emergencies Ministry highlights the importance of early warning systems in mitigating the risks associated with seismic events. These systems rely on real-time data from seismometers and ocean buoys to assess the likelihood of tsunamis and communicate warnings to affected populations. In this case, the timely issuance and subsequent downgrading of the tsunami warning helped prevent panic while ensuring that residents remained vigilant.
Historical Context: Kamchatka’s Seismic Past
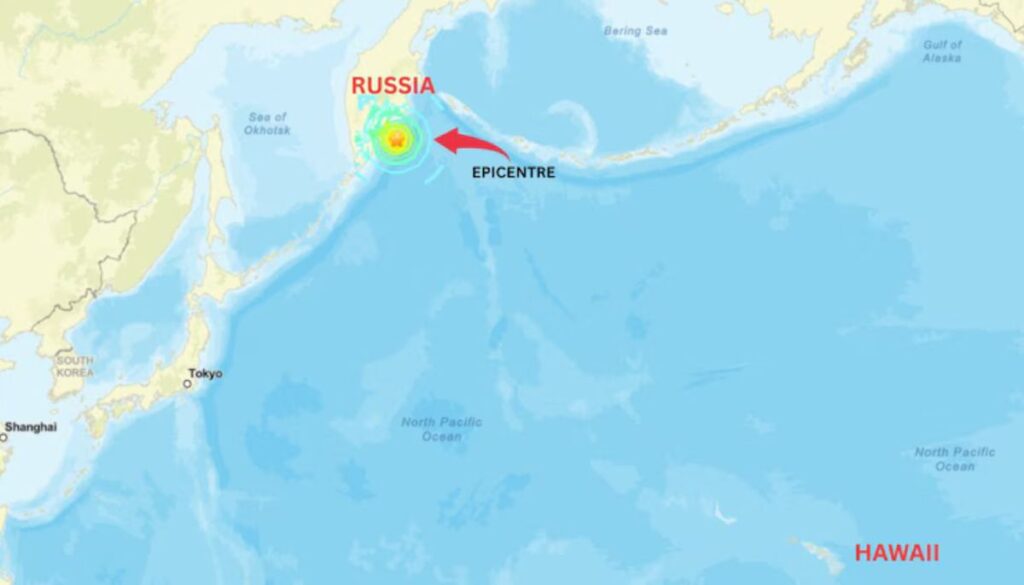
The Kamchatka Peninsula has a long history of significant seismic activity. One of the most notable events occurred on November 4, 1952, when a massive 9.0-magnitude earthquake struck the region. Although that quake caused damage in Kamchatka, it resulted in no reported deaths locally. However, it generated devastating 9.1-meter (30-foot) tsunami waves that struck Hawaii, causing significant destruction thousands of miles away. This historical event underscores the far-reaching impacts that earthquakes in the Kamchatka region can have, even when local damage is minimal.
The 2025 earthquakes, while not as severe as the 1952 event, serve as a reminder of the region’s vulnerability to seismic hazards. The Kamchatka Peninsula lies along a subduction zone, where the Pacific Plate is forced beneath the North American Plate, creating intense geological pressure. This tectonic activity is responsible for the region’s frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, making it one of the most seismically active areas in the world.
Impact and Immediate Aftermath
As of the latest reports, there have been no immediate casualties or significant damage reported from the July 20, 2025, earthquakes. The relatively remote location of the epicenter, 144 kilometers offshore, likely contributed to the lack of widespread destruction in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky and surrounding areas. However, the event has prompted authorities to assess infrastructure and coastal defenses to ensure they are prepared for any aftershocks or future seismic activity.
Residents of coastal communities were advised to avoid the shoreline and seek higher ground as a precautionary measure. The Emergencies Ministry’s warning emphasized the importance of staying alert, as even small tsunami waves can pose risks to low-lying areas. Local authorities have also been working to educate the public about earthquake and tsunami preparedness, including the importance of having emergency kits, evacuation plans, and access to reliable communication channels.
The Role of Early Warning Systems
The rapid response to the Kamchatka Peninsula earthquake and tsunami warning demonstrates the critical role of early warning systems in protecting lives and property. Organizations like the PTWC and the USGS play a vital role in monitoring seismic activity and issuing timely alerts. These systems use advanced technology to detect earthquakes and assess their potential to generate tsunamis, providing critical information to governments, emergency services, and the public.
In the case of the 2025 Kamchatka earthquakes, the PTWC’s ability to quickly downgrade the tsunami warning from “major waves” to “up to one meter” helped prevent unnecessary panic while ensuring that residents remained cautious. This balance is essential in regions like Kamchatka, where seismic events are common but not all pose an immediate threat. Continued investment in early warning systems, as well as public education about earthquake and tsunami preparedness, is crucial for minimizing the risks associated with these natural disasters.
Preparing for Future Seismic Events
The recent earthquakes serve as a wake-up call for residents and authorities in the Kamchatka Peninsula and other seismically active regions. While the 2025 events did not result in significant damage or loss of life, they highlight the importance of preparedness. Here are some key steps that individuals and communities can take to stay safe during earthquakes and potential tsunamis:
- Develop an Emergency Plan: Families and communities should have a clear plan for what to do in the event of an earthquake or tsunami. This includes identifying safe evacuation routes and meeting points.
- Assemble an Emergency Kit: Keep a supply of essentials such as food, water, first aid supplies, flashlights, and batteries in an easily accessible location.
- Stay Informed: Monitor local news and official channels for updates on seismic activity and warnings. Sign up for alerts from organizations like the PTWC or local emergency services.
- Secure Your Home: Anchor heavy furniture, secure appliances, and reinforce buildings to withstand shaking.
- Know the Signs of a Tsunami: A sudden rise or fall in sea level, unusual ocean sounds, or strong ground shaking can indicate a potential tsunami. If you notice these signs, move to higher ground immediately.
By taking these proactive measures, individuals and communities can reduce the risks associated with earthquakes and tsunamis, ensuring a safer and more resilient future.
The Global Significance of the Kamchatka Earthquakes
The Kamchatka Peninsula earthquake and tsunami warning of 2025 is not just a local concern but a reminder of the interconnected nature of our planet’s geological systems. Earthquakes in this region can have far-reaching effects, as demonstrated by the 1952 tsunami that impacted Hawaii. The Pacific Ring of Fire, which includes Kamchatka, is responsible for approximately 90% of the world’s earthquakes, making it a critical area for scientific study and monitoring.
Researchers and seismologists will likely analyze the 2025 Kamchatka earthquakes to better understand the region’s tectonic activity and improve predictive models. This information can help refine early warning systems and enhance global preparedness for seismic events. Additionally, the event underscores the importance of international collaboration in addressing natural disasters, as tsunamis and earthquakes often have impacts that cross national borders.
Russia Kamchatka Earthquake & Tsunami Alert: All You Need to Know

| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What happened in Kamchatka, Russia on July 21, 2025? | Two powerful earthquakes struck off the coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula, the strongest being a magnitude 7.4 quake, followed by a 6.7 quake moments earlier. |
| Where did the 7.4 magnitude quake strike? | It occurred 144 kilometers (89 miles) east of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, at a depth of 20 kilometers (12 miles) beneath the Pacific Ocean. |
| Was there a tsunami warning issued? | Yes, the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center initially issued a tsunami warning but later downgraded it, stating that waves up to 1 meter (3.3 feet) may occur. |
| Did the Russian government respond to the quake? | Yes, Russia’s Emergencies Ministry also issued a tsunami warning, urging people living in coastal settlements to stay away from the shore. |
| Were there any casualties or damage reported? | As of now, there have been no reports of casualties or major structural damage. |
| Is there a tsunami threat now? | No, the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center later clarified that there is no current threat of a major tsunami. |
| How strong was the second earthquake? | The earlier quake measured 6.7 on the Richter scale and occurred just minutes before the 7.4 magnitude event. |
| What is the significance of Kamchatka in terms of seismic activity? | Kamchatka lies along the Pacific Ring of Fire, a major seismic belt where earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are frequent. |
| What historic quake is Kamchatka known for? | On November 4, 1952, a 9.0 magnitude quake struck Kamchatka, causing 30-foot waves in Hawaii but no reported deaths. |
| What should local residents do now? | Stay alert to official guidance, avoid coastal areas, and monitor emergency updates from Russian authorities and international seismic monitoring centers. |
| Are aftershocks expected? | Aftershocks are common following a major quake. Residents and authorities are advised to remain vigilant for further seismic activity. |
| What agencies are monitoring the situation? | The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center (PTWC), and Russia’s Emergencies Ministry are actively monitoring the situation. |
Conclusion: Staying Vigilant in a Dynamic World
The Kamchatka Peninsula earthquake and tsunami warning of July 20, 2025, serves as a stark reminder of the power of nature and the importance of preparedness. While the region was fortunate to avoid significant damage or loss of life, the event highlights the need for continued vigilance in seismically active areas. By leveraging advanced warning systems, educating the public, and implementing robust preparedness measures, communities can mitigate the risks of earthquakes and tsunamis.
As the Kamchatka Peninsula recovers from this seismic event, the focus remains on ensuring the safety of residents and strengthening resilience for the future. For those living in or visiting seismically active regions, staying informed and prepared is the best defense against the unpredictable forces of nature.
Note: All information and images used in this content are sourced from Google. They are used here for informational and illustrative purposes only.
Russia Kamchatka Earthquake and Tsunami Warning: All FAQs Answered
What triggered the tsunami warning off Russia’s Pacific coast?
Two strong offshore earthquakes struck near the Kamchatka Peninsula on Sunday, July 21, 2025. The larger of the two had a magnitude of 7.4, while the earlier quake registered 6.7. These events prompted the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center (PTWC) to issue a tsunami threat advisory for nearby coastal regions.
Where did the strongest earthquake occur?
The strongest quake, with a magnitude of 7.4, occurred at a depth of 20 kilometers and was centered 144 kilometers east of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, a coastal city with a population of about 180,000 people. The information was confirmed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
Was a tsunami actually generated?
No large tsunami waves were observed. While the initial alert warned of the potential for major waves, the PTWC later downgraded the warning. It stated that tsunami waves of up to one meter (about 3.3 feet) could be expected in coastal areas but were unlikely to cause widespread damage.
Is there still a tsunami threat?
The threat has been downgraded. As of the latest updates, there is no ongoing tsunami danger. Authorities have advised coastal residents to remain cautious but confirmed that the immediate risk has passed.
How did Russian authorities respond?
Russia’s Emergencies Ministry also issued a tsunami warning after the second quake. Citizens in coastal settlements were urged to stay away from the shoreline as a precautionary measure. No evacuation orders were issued, but local authorities advised vigilance.
Have there been any casualties or damage?
There are no reports of injuries, fatalities, or major structural damage at this time. Emergency services remain on alert, and monitoring efforts are continuing to ensure the safety of residents.
Is Kamchatka prone to earthquakes?
Yes, the Kamchatka Peninsula lies in the Pacific Ring of Fire, one of the most active seismic zones on the planet. This region frequently experiences earthquakes and volcanic activity due to the movement of tectonic plates.
Has Kamchatka experienced similar earthquakes in the past?
Yes. On November 4, 1952, Kamchatka was hit by a magnitude 9.0 earthquake that generated 30-foot tsunami waves in Hawaii. Although damage was reported, no deaths occurred. That event remains one of the most significant in Pacific seismic history.
How many earthquakes occurred on July 21?
A total of five offshore earthquakes were recorded near the Kamchatka Peninsula within several hours. The most powerful reached a magnitude of 7.4, with the earlier one at 6.7. These quakes were followed by several smaller tremors, as is typical in such events.
Are aftershocks expected?
Yes. Aftershocks are common following major earthquakes, especially in tectonically active regions. Residents are advised to remain cautious and to be prepared for additional tremors.
Who is monitoring the situation?
The situation is being closely monitored by multiple agencies, including:
- United States Geological Survey (USGS)
- Pacific Tsunami Warning Center (PTWC)
- Russia’s Emergencies Ministry
These organizations are providing real-time updates and coordinating with local authorities.
What should residents do?
Residents in the affected regions are advised to:
- Avoid beaches and low-lying coastal zones until official clearance is given
- Follow updates from local and international emergency services
- Prepare for possible aftershocks and practice safety protocols
- Remain calm and avoid spreading unverified information







Leave a Reply